หลังจากที่ หัดใช้ Route และ View เบื้องต้น แล้ว ในตอนนี้เรามาดูวิธีเขียน Laravel เพื่อเชื่อมต่อฐานข้อมูลกัน
โดยจะใช้วิธีการทำ migrate หรือ migration ของ Laravel ซึ่งเปรียบเสมือนเป็นการจัดการควบคุมเวอร์ชั่นของฐานข้อมูล (version control ของ database) เพื่อให้ laravel ทราบว่า โครงสร้างตารางที่ใช้นั้นมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงไปอย่างไร และจะสร้าง แก้ไข หรือลบไฟล์ที่เกี่ยวข้องตามโครงสร้างที่เปลี่ยนไปได้โดยอัตโนมัติ
แล้วใช้ Eloquent ORM เพื่อดึงข้อมูลออกมา
คอนฟิกฐานข้อมูล
เริ่มจากการสร้าง database เพื่อใช้ทดสอบ แล้ว GRANT สิทธิ์เพื่อกำหนดชื่อผู้ใช้ (user) และรหัสผ่าน (password) ในการเชื่อมต่อเข้าฐานข้อมูล
mysql> CREATE DATABASE laravel; mysql> GRANT ALL ON laravel.* TO 'laravel'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'laravel-password';
หมายเหตุ ชื่อฐานข้อมูลหรือชื่อผู้ใช้ไม่จำเป็นต้องเป็นชื่อ laravel จะเป็นชื่ออะไรก็ได้ แต่ต้องตรงกับไฟล์คอนฟิกที่เราจะแก้ไขต่อไป
cd เข้าไปในไดเร็กทอรีที่สร้างแอพไว้
[alice@cent6-php ~]$ cd /var/www/html/blog/
ไฟล์คอนฟิกในการเชื่อมฐานข้อมูล จะถูกกำหนดอยู่ในไฟล์ app/config/database.php
Laravel รอบรับฐานข้อมูลได้หลายชนิดทั้ง mysql, sqlite, pgsql ในที่นี้จะกำหนดค่า ‘default’ หรือชนิดของฐานข้อมูลที่จะใช้เป็น mysql
ถ้ากำหนดค่าเป็น mysql ก็ต้องแก้ไขค่าตัวแปรที่ใช้เชื่อมฐานข้อมูลใน array [‘connections][‘mysql’] โดยแก้ไขค่าต่างๆ ให้ตรงกับที่ GRANT สิทธิ์ไว้ตอนแรก
ตัวอย่างการแก้ไขไฟล์
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ vi app/config/database.php
...
/*
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Default Database Connection Name
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| Here you may specify which of the database connections below you wish
| to use as your default connection for all database work. Of course
| you may use many connections at once using the Database library.
|
*/
'default' => 'mysql',
...
/*
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Database Connections
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| Here are each of the database connections setup for your application.
| Of course, examples of configuring each database platform that is
| supported by Laravel is shown below to make development simple.
|
|
| All database work in Laravel is done through the PHP PDO facilities
| so make sure you have the driver for your particular database of
| choice installed on your machine before you begin development.
|
*/
'connections' => array(
'sqlite' => array(
'driver' => 'sqlite',
'database' => __DIR__.'/../database/production.sqlite',
'prefix' => '',
),
'mysql' => array(
'driver' => 'mysql',
'host' => 'localhost',
'database' => 'laravel',
'username' => 'laravel',
'password' => 'laravel-password',
'charset' => 'utf8',
'collation' => 'utf8_unicode_ci',
'prefix' => '',
),
รัน migrate เพื่อแก้ไขโครงสร้างฐานข้อมูล
รัน php artisan โดยเริ่มต้นระบุออปชั่นเป็น migrate:make ตามด้วยชื่ออะไรก็ได้ เพื่อจะสร้างไฟล์คลาส
คำแนะนำ ให้ตั้งชื่อให้สอดคล้องกับสิ่งที่กำลังจะแก้ไขโครงสร้างฐานข้อมูล เพราะชื่อนี้จะนำไปใช้ในการตั้งชื่อคลาสด้วย เข่นในที่นี้เราจะสร้างตาราง users ขึ้นมา เราก็ตั้งเป็น create_users_table
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ php artisan migrate:make create_users_table Created Migration: 2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table Generating optimized class loader Compiling common classes Compiling views
คำสั่ง php artisan migrate:make จะสร้างไฟล์ class ขึ้นมาไว้ในไดเร็กทอรี app/database/migrations/
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ ls -l app/database/migrations/ total 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 alice users 326 Jan 8 20:56 2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table.php
ดูไฟล์ class ได้ สังเกตว่า Laravel จะแปลงชื่อที่ตั้งไว้เป็นชื่อคลาส โดยตัดเครื่องหมาย _ ออก พร้อมเปลี่ยนแต่ละคำเป็นตัวอักษรพิมพ์ใหญ่ (CamelCase)
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ cat app/database/migrations/2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table.php ... use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint; use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration; class CreateUsersTable extends Migration { /** * Run the migrations. * * @return void */ public function up() { // } /** * Reverse the migrations. * * @return void */ public function down() { // } }
ไฟล์นี้จะเป็นตัวกำหนดโครงสร้างฐานข้อมูลที่เปลี่ยนไป
เมธอด up() ไว้สำหรับการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้างข้อมูล เข่นเพิ่ม ลบ แก้ ตารางหรือฟิลด์ต่างๆ
เมธอด down() จะยกเลิกการเปลี่ยนแปลง (rollback) สิ่งที่ถูกเปลี่ยนไปโดยเมธอด up()
ตัวอย่างด้านล่าง ในเมธอด up() จะสร้างตารางชื่อ “users” ประกอบด้วยฟิลด์ id, email, name, timestamps()
หมายเหตุ timestamps() จะเป็นการสร้างฟิลด์ชื่อ created_at และ updated_at ชนิด timestamp เพื่อเก็บเวลาที่แต่ละเรคอร์ด (rows) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง
ส่วนเมธอด down() เราก็กำหนดไว้เป็นยกเลิกการสร้างตาราง หรือ drop ตารางที่สร้างไว้นั่นเอง
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ vi app/database/migrations/2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table.php
...
class CreateUsersTable extends Migration {
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
// create table
Schema::create('users', function($table)
{
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('email')->unique();
$table->string('name');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
// drop table
Schema::drop('users');
}
}
หลังจากแก้ไขไฟล์คลาสเรียบร้อยแล้ว รัน php artisan อีกครั้ง แต่ครั้งนี้ระบุแค่ออปชั่น migrate
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ php artisan migrate ************************************** * Application In Production! * ************************************** Do you really wish to run this command? y Migration table created successfully. Migrated: 2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table
ตอบ y เพื่อยืนยัน
ผลลัพธ์ที่ได้ จากการรัน migrate จะมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้างตารางตามที่กำหนดไว้ในเมธอด up()
mysql> SHOW TABLES; +-------------------+ | Tables_in_laravel | +-------------------+ | migrations | | users | +-------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
ตาราง migrations เป็นตารางพิเศษ จะเก็บประวัติการรัน migrate เพื่อเวลาย้อนกลับ (rollback) จะได้ทำอย่างถูกต้อง
mysql> SELECT * FROM migrations; +--------------------------------------+-------+ | migration | batch | +--------------------------------------+-------+ | 2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table | 1 | +--------------------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ลองดูตาราง users ที่ถูกสร้างขึ้น
mysql> DESCRIBE users; +------------+------------------+------+-----+---------------------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +------------+------------------+------+-----+---------------------+----------------+ | id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | email | varchar(255) | NO | UNI | NULL | | | name | varchar(255) | NO | | NULL | | | created_at | timestamp | NO | | 0000-00-00 00:00:00 | | | updated_at | timestamp | NO | | 0000-00-00 00:00:00 | | +------------+------------------+------+-----+---------------------+----------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
ตาราง users ยังไม่มีข้อมูลใดๆ
mysql> SELECT * FROM users; Empty set (0.00 sec)
ถ้าตารางที่สร้างไว้ไม่ถูกต้อง หรือต้องการยกเลิก สามารถรัน rollback เพื่อเรียกเมธอด down() ได้
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ php artisan migrate:rollback ************************************** * Application In Production! * ************************************** Do you really wish to run this command? y Rolled back: 2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table
ตาราง users ก็จะถูก drop ไป
mysql> SHOW TABLES; +-------------------+ | Tables_in_laravel | +-------------------+ | migrations | +-------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * FROM migrations; Empty set (0.00 sec)
รัน migrate อีกครั้ง เพื่อสร้างตาราง users กลับมา
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ php artisan migrate ************************************** * Application In Production! * ************************************** Do you really wish to run this command? y Migrated: 2015_01_08_135602_create_users_table mysql> SHOW TABLES; +-------------------+ | Tables_in_laravel | +-------------------+ | migrations | | users | +-------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
การใช้ Eloquent ORM เพื่อดึงข้อมูล
หลังจากได้ตารางแล้ว เราลองมาเขียน Laravel เพื่อดึงข้อมูลจากฐานข้อมูลกัน
ใน Laravel หรือ MVC ส่วนของโปรแกรมที่จะใช้ในการเชื่อมต่อกับฐานข้อมูลเราจะเรียกว่า Models โดย Laravel จะกำหนดให้สร้างเป็นไฟล์คลาสไว้ในไดเร็กทอรี app/models/
ตัวอย่างเช่น ต้องการเชื่อมกับตาราง users แนะนำให้ตั้งชื่อคลาส User และสร้างไฟล์คลาสชื่อ User.php
ตัวอย่างของไฟล์คลาส User.php ด้านล่างนี้ ติดมาจากการติดตั้ง laravel อยู่แล้ว ไม่ต้องแก้ไขอะไร
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ vi app/models/User.php ... use Illuminate\Auth\UserTrait; use Illuminate\Auth\UserInterface; use Illuminate\Auth\Reminders\RemindableTrait; use Illuminate\Auth\Reminders\RemindableInterface; class User extends Eloquent implements UserInterface, RemindableInterface { use UserTrait, RemindableTrait; /** * The database table used by the model. * * @var string */ protected $table = 'users'; /** * The attributes excluded from the model's JSON form. * * @var array */ protected $hidden = array('password', 'remember_token'); }
โดยดีฟอลต์ Laravel จะทำการ map ชื่อคลาสที่ตั้งไว้ใน models กับชื่อตาราง table ในฐานข้อมูลโดยเติมตัว (s) โดยอัตโนมัติ เช่นในที่นี้ชื่อคลาส User จะถูกแปลงเป็นชื่อตาราง users แต่ถ้าไม่ตรงตามรูปแบบนี้เราสามารถกำหนดไว้ในตัวแปรหรือพรอพเพอรตี้ $table ได้
แก้ไขไฟล์ routes.php เพื่อให้เวลาเรียกพาธ /users ให้มาเรียกใช้ models ที่ชื่อว่า User
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ vi app/routes.php ... /* |-------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Application Routes |-------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | Here is where you can register all of the routes for an application. | It's a breeze. Simply tell Laravel the URIs it should respond to | and give it the Closure to execute when that URI is requested. | */ Route::get('/', function() { return View::make('hello'); }); Route::get('users', function() { $users = User::all(); return View::make('users')->with('users', $users); });
คำอธิบาย User::all() เป็นการเรียกคลาส User ใน models เมธอด all() จะเป็นการแสดงทุกเรคอร์ดในตาราง users ซึ่ง Laravel จะจัดการให้เองโดยอัตโนมัติ
ส่วน View::make(‘users’)->with(‘users’, $users) จะเป็นการส่งค่าที่เก็บในตัวแปร $users เข้าไปใน views ที่ชื่อ users
จาก หัดใช้ Route และ View เบื้องต้น เราต้องแก้ไขไฟล์ users.blade.php เพิ่มเติม เพื่อให้สามารถวนลูปเรคอร์ดที่ได้จากตาราง users
ตัวอย่างการแก้ไขไฟล์
[alice@cent6-php blog]$ vi app/views/users.blade.php
@extends('layout')
@section('content')
@foreach($users as $user)
<p>{{ $user->name }}</p>
@endforeach
@stop
ส่วนไฟล์ layout.blade.php เหมือนเดิม
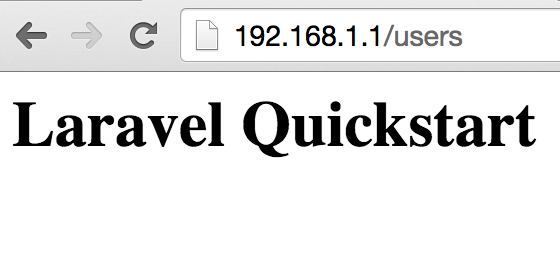
ทดลองเปิดบน browser
เนื่องจากตาราง users ยังไม่มีข้อมูลอะไร
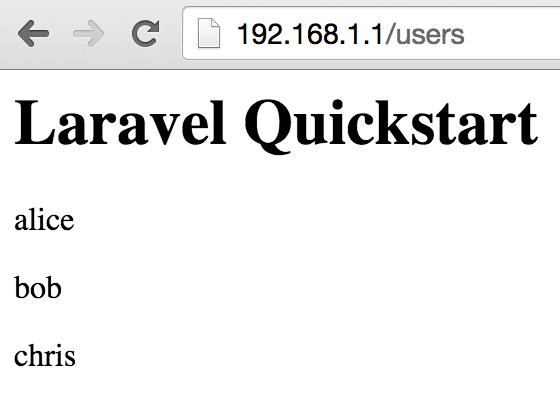
ทดลองใส่ข้อมูลเข้าไปในตาราง users
mysql> INSERT INTO users (email, name) VALUES ('alice@example.com', 'alice');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO users (email, name) VALUES ('bob@example.com', 'bob');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO users (email, name) VALUES ('chris@example.com', 'chris');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
ลองเปิดบน browser อีกครั้ง